What Exactly Is CBD Oil and how does CBD Work on the Brain and Body?
The inside scoop on the Human Endocannabinoid System: The endocannabinoid system (ECS) consists of numerous cannabinoid receptors. CBD stands for cannabidiol. A naturally occurring cannabinoid, CBD oil is derived from hemp. There are over 100 cannabinoids found in the hemp plant, alone. Unlike THC, CBD will not get you high, CBD has non-psychoactive properties. Cannabinoids are also found in our bodies. Cannabinoid receptors are located throughout the body—part of the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in a variety of physiological processes including appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory. Before we dive into how CBD works on our brain and body, let’s briefly review what CBD is. We’ve touched on it several times, but it never hurts to review. CBD, short for Cannabidiol, is one of the hundreds of cannabinoids present in the Cannabis plant. Different strains produce differing levels of CBD. Cannabis Sativa, commonly known as hemp, is high in CBD and low in THC. Conversely, Cannabis Indica is low in CBD and high in THC, the most famous member of the cannabinoid family and the one responsible for the feeling of getting high. CBD is recommended by countless top medical doctors throughout the world to help relieve many ailments and health conditions. CBD comes in many forms—CBD oil, CBD capsules, CBD topicals, and more. CBD is successfully used in an FDA-approved drug to treat severe kinds of epilepsy in children. Research shows that CBD can also help with various conditions, such as seizures, pain, inflammation, depression, anxiety, mental disorders, nausea, skin inflammation, migraines, and more.
How does CBD work?
Your body already has an intricate Endocannabinoid System(ECS) that affects several different areas and functions. The ECS is loaded with “receptors” sites that await cannabinoid molecules presence. When the cannabinoid nears, the receptor will bind it to itself, creating a sophisticated chemical interaction that modern science is only just beginning to scratch the surface of understanding. Unlike THC, CBD does not make you feel high — but don’t think that a lack of psychoactive or intoxicating effects means that nothing is occurring. On the contrary, it’s very clear that there are many chemical responses that occur when CBD binds to those cannabinoid receptors. That being said, the endocannabinoid system is ubiquitous in the human body, affecting nearly all major functions in some way (especially homeostatic regulation). Because of this, getting at the inside scoop on the Human Endocannabinoid System is quite a task to discern..
What is the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?The Endocannabinoid System (ECS), an extension of our Central Nervous System, that is composed of receptors, neurotransmitters and enzymes. The ECS interacts with Cannabinoids found in the Cannabis plant and Endocannabinoid that are produced by our own bodies.
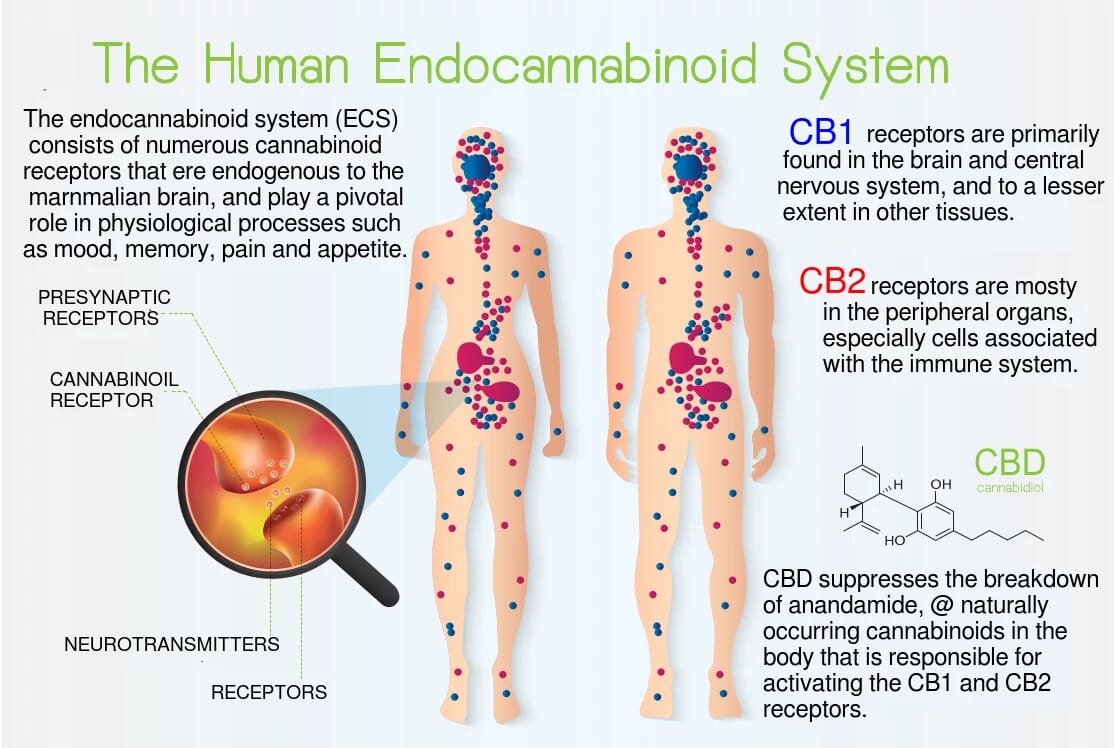 The Human Endocannabinoid System
The Human Endocannabinoid SystemThere are two main endocannabinoid receptors:
- CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system.
- CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system.
CBD’s Effect on the Brain
Where the research begins to get really interesting is when discussing CBD’s effects on non-cannabinoid receptors and other independent cell pathways. CBD can increase levels of the body’s naturally-produced cannabinoids (known as endocannabinoids) by inhibiting the enzymes that break them down. Scientists call this a reuptake and breakdown inhibitor.
Let’s dig into that a little deeper. For example, our body makes an endocannabinoid neurotransmitter known as anandamide, binding to the CB1 and CB2 receptors as described above. Essentially, CBD interrupts the process of breaking down the neurotransmitter by hitching a ride on the same fatty acids that would normally carry the chemical to the cell, preventing the neurotransmitter from catching that same ride. In that way, CBD acts as a reuptake inhibitor, increasing the levels of the anandamide in our body and enhancing the protective effects against seizures. In fact, studies have shown there are multiple targets for CBD in the brain that working together can act on lessening seizure activity. Currently, the FDA has approved highly purified Cannabidiol (CBD) under the name Epidiolex® in the United States and as EPIDYOLEX in the EU. Epidiolex has been approved as a treatment for seizures associated with epileptic disorders. (Making this the first and only FDA-approved use for CBD).
The anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety properties of CBD are somewhat attributed to this same phenomenon. CBD also acts as a reuptake inhibitor on adenosine. By interrupting the breakdown process, CBD can increase levels of adenosine in the brain and the regulation of adenosine receptors. (Remember we talked about non-cannabinoid receptors?) So why is that important? These receptors target cardiovascular function (including oxygen intake and blood flow) and have anti-inflammatory effects. More adenosine equals less inflammation. Source
Studies have also discovered that CBD targets another non-cannabinoid serotonin-specific receptor. Just as a refresher, serotonin is the primary hormone responsible for mood stabilization and feelings of overall happiness and assists with sleeping, eating, and the digestive process. CBD is known as a “modest affinity agonist,” which is fancy wording for something that initiates a physiological response in our body when combined with the receptors we’ve been discussing. Source. English pharmacologist and noted cannabinoid researcher Professor Roger Pertwee discusses the potential of CBD activating these serotonin receptors. (Via Leafly).
“It’s apparent ability to enhance the activation of serotonin 1A receptors supports the possibility that it could be used to ameliorate disorders that include: opioid dependence, neuropathic pain, depression and anxiety disorders, nausea and vomiting (e.g. from chemotherapy), and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.” So let’s review:
- Humans possess an endocannabinoid system designed to help regulate chemical neurotransmitters within the central nervous system.
- CBD works within the endocannabinoid system to interrupt the breakdown of the homegrown chemicals, increasing the levels of these naturally occurring compounds.
- The resultant increase creates an additive effect-meaning the CBD can increase the physiological benefits already occurring from the various neurotransmitters.
What does all this mean? Well, there is still a lot of research to be done. While we know generally how it works, the clinical applications are still being studied as the largest body of work has been done in animals, not humans. Some good news? As we mentioned above, the FDA has approved CBD in the form of Epidiolex to treat certain seizure disorders. Research is continuing on the complex ability of CBD to precisely target the various receptors we’ve discussed (plus more) and what the therapeutic applications are for humans.
Part of the criticism surrounding CBD and its benefits is based on the lack of regulation surrounding the industry. As research continues to further our knowledge and understanding of the inside scoop on the Human Endocannabinoid System, and this multi-tasking molecule and its powerful impact on our brain and body, make sure you are still abiding by our recommendations on purchasing high-quality CBD hemp oil products free from chemical additives and false advertising.
FDA DISCLOSURE
The statements made regarding these products have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. The efficacy of these products has not been confirmed by FDA-approved research. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. All information presented here is not meant as a substitute for or alternative to information from health care practitioners. Please consult your health care professional about potential interactions or other possible complications before using any product. The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act requires this notice.

